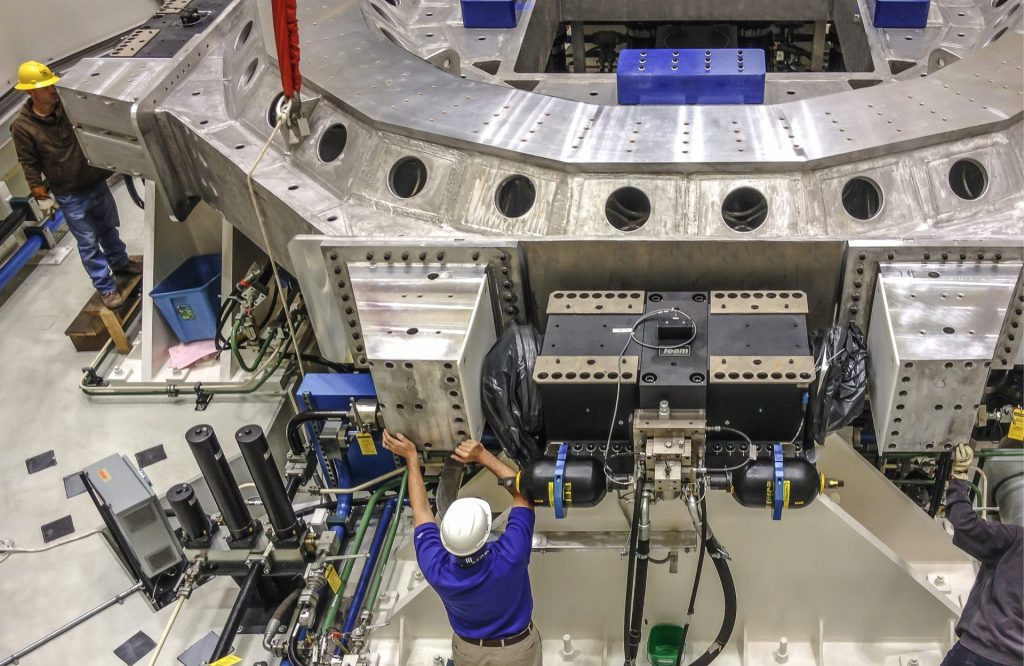
Testing is Scheduled for Mid-to-Late December
Dream Chaser joins Sierra Space’s cargo module, Shooting Star™, which arrived at NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility – a remote campus of Glenn Research Center in Sandusky, Ohio – in November. The two vehicles are set to be stacked in launch configuration and undergo rigorous environmental testing, starting in the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF). The tests will subject them to the extreme conditions of launch vibrations on the world’s most powerful spacecraft shaker table.
Sierra Space is ushering in the next era of space exploration with its revolutionary fleet of Dream Chaser® space planes.

About the MVF
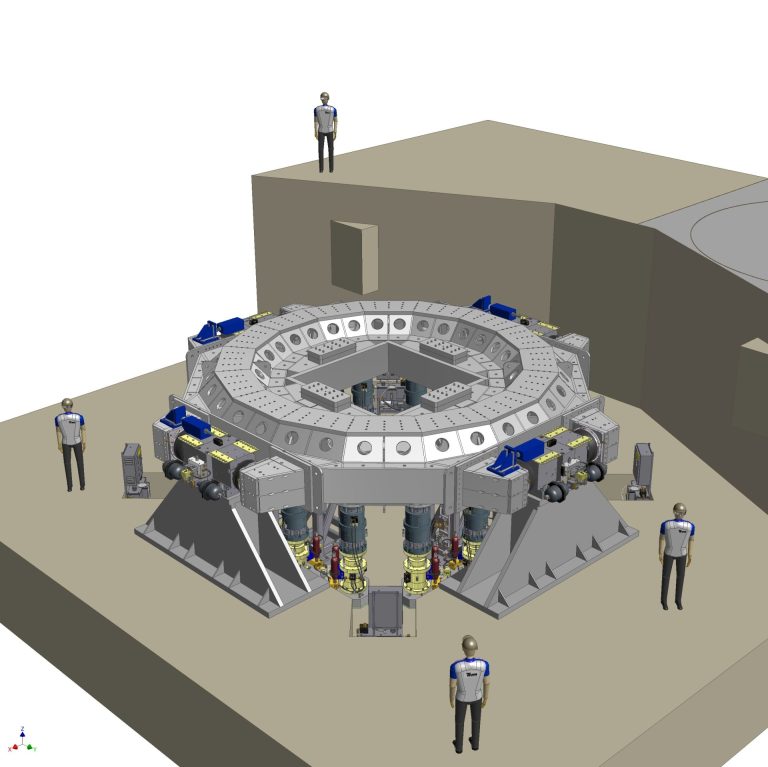
The MVF is a three-axis, 6-degree-of-freedom, servohydraulic, sinusoidal base-shake vibration system – designed, engineered, and built by Team Corporation – located within the same Vibroacoustic High Bay as the Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility (RATF) on the west side of the vacuum chamber. The proximity to the RATF allows shared use of the hydraulic system, safety systems, high-speed data acquisition system and surveillance system. The MVF system consists of reaction mass, 4 horizontal servohydraulic actuators, 16 vertical servohydraulic actuators mounted on double-spherical couplings, an aluminum table, a hydraulic supply system, table control system (TCON), vibration control system (VCON) and the same FCS used by the RATF.
The MVF reaction mass includes an embedded steel plate for modal testing. The 2,100,000-kg (4,650,000-lb) reaction mass is used to resist the vibratory energy from the hydraulic actuators, table and test article, transferring the energy into the shale bedrock foundation. The reaction mass has been sized such that it has sufficient inertia mass and stiffness to react against the forces applied by the actuator/couplings during sine vibration testing. The reaction mass has been designed to accommodate future growth in vibration system and test article mass. The existing actuator and table design is for sine sweep capability of 0 to 1.25g (peak), from 5 to 150 Hz in the vertical axis and 0 to 1.0g from 5 to 150 Hz in each of the horizontal axes for a test article mass of 34,000 kg (75,000 lb) with a center of gravity elevation of 7 m (23 ft).
The MVF is controlled by a Data Physics Multi-Shaker Controller with 80 input channels that can be used in any combination of Control, Limit, or Measurement channels. This controller is capable of sinusoidal control in three independent axes.
The MVF system design uses a large aluminum table approximately 6.7 m (22 ft) in diameter with a 0.61-m (2-ft) wide annular mounting surface centered about a 5.5-m (18-ft) nominal diameter. Table weight is partially off-loaded from the system via four inflatable airbags.
The table vertical actuation is provided by 16 Team Corporation hydraulic cylinder actuators attached to the reaction mass, onto which 16 double-spherical couplings are attached. The vertical actuator assemblies provide the controlled vertical sine vibration, enable horizontal vibration and provide overturning constraints during horizontal vibration. The table rests on the double-spherical couplings. The double-spherical couplings couple each vertical actuator to the table and provide high-axial stiffness to deliver the vertical vibratory force during vertical excitation. Each double-spherical coupling has internal pressure sensors to enable the vibration controller to limit forces.
Four horizontal actuators provide the controlled horizontal sine vibration and comprise two single-ended pistons, which maintain outward force through hydrostatic pad-bearings to the table. The horizontal actuator assemblies provide vertical alignment during vertical actuation. The system is designed to permit testing in three independent axes without removing or lifting the test article from the table.
Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) Highlights:
• The world’s most powerful vibration test system
• 16 vertical actuators and 4 lateral actuators
• 75,000 lbs. max test article mass
• 77 ft. test article height
• 4,650,000 lbs. seismic mass
• Frequency performance from 5-150 Hz.
• Maximum vertical static force 720,000 lbs.
| Parameters | |
| Max. test article mass | 34,000 kg (75,000 lb) |
| Max. Cg above table | 7.2 m (23.6 ft) |
| Seismic mass | 2,100,000 kg (4,650,000 lb) |
| Max. vertical static force | 3,203 kN (720,000 lb) |
| Max. vertical dynamic displacement (peak-to-peak) | 3.18 cm (1.25 in.) |
| Max. vertical velocity | 41.7 cm/s (16.4 in./s) |
| Max. lateral static force | 1,139 kN (256,200 lb) |
| Max. lateral dynamic displacement (peak-to-peak) | 3.048 cm (1.2 in.) |
| Max. lateral velocity | 33.8 cm/s (13.3 in./s) |
| Sine sweep rate | Dwell to 4 oct/min |
| Max. test article height | 23.5 m (77 ft) |
| Sine sweep rate | Dwell to 4 oct/min |
| Physical Characteristics | |
| Table mounting bolt-circle diam. | 518.16, 538.48, 558.8, and 579.12 cm (204, 212, 220, and 228 in.) |
| Max. test article height | 23.5 m (77 ft) |
| Max. test article height below crane bridge | 20.4 m (67 ft) |
| Sine sweep rate | Dwell to 4 oct/min |
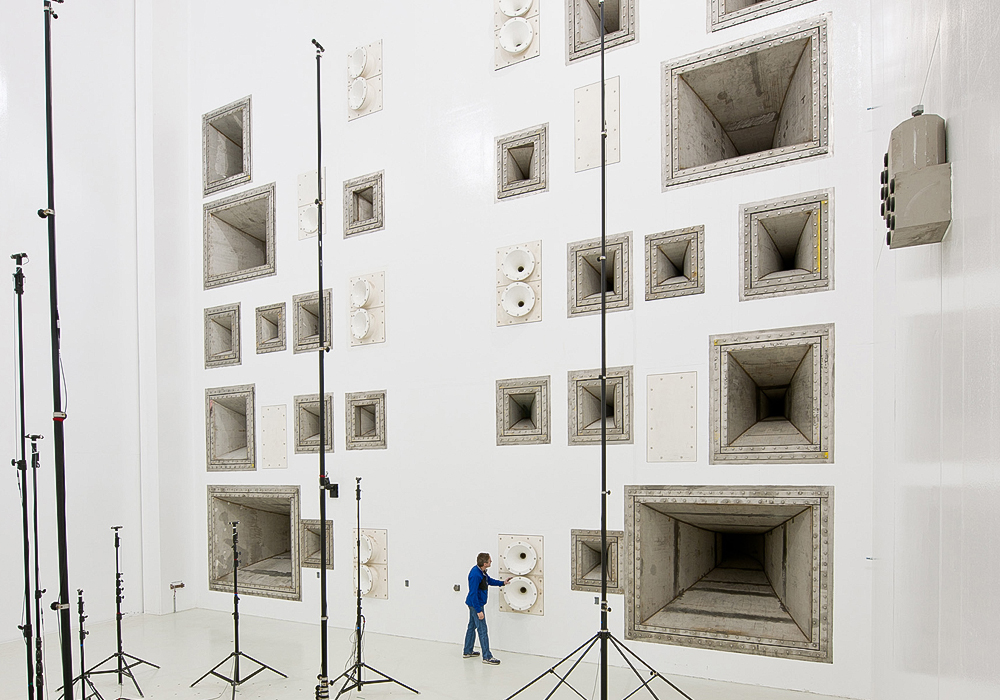

Acoustic Testing in the RATF
The Reverberant Acoustic Test Facility (RATF) at NASA’s Space Environments Complex (SEC) – the largest acoustic test facility in the world – is a chamber that features a wall studded with numerous rows of powerful acoustic horns. Nitrogen gas flowing through hydraulic actuators that are turning on and off at incredibly rapid speeds create the horns’ horrendous acoustic assault. Capable of bathing test articles with an overall acoustic sound pressure level of 163 decibels, it is by far the most powerful acoustic chamber in the world. This facility features 23 Team Acoustic Modulators, producing over 4.5 Megawatts of sound power, requiring 70,000 scfm gas flow at 200 psi.
Take a virtual tour of the NASA test facility
The Space Environments Complex (SEC) houses the largest and most powerful space environment simulation facilities in the world. This includes the largest space simulation vacuum chamber, most powerful spacecraft acoustic test chamber and the world’s highest capacity and most powerful spacecraft shaker system.



